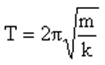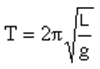GCSE物理:什么是简谐振动simple harmonic motion(SHM)?
l Oscillation振荡
指某一可观测量的值关于中心值(常为平衡点)往复变化,或可观测量在两个态或多个态之间往复变化,常指随时间的变化。常见的例子是单摆和交流电。振荡也常称作振动。
完成一次完整的机械振动所用的时间叫做一个周期 time period, T. 单位是秒。
If a number of oscillations are involved we can work out the time period by dividing the total time taken by the number of oscillations completed:
如果题中给出一个包含很多次振荡次数的时间,那么周期就是:
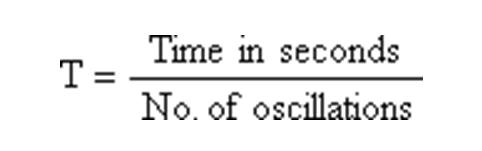
The frequency, f, 单位时间内完成振动的次数,单位是赫兹 hertz (Hz).
The frequency and the period can therefore be related as:
周期与频率的关系:
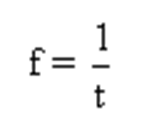
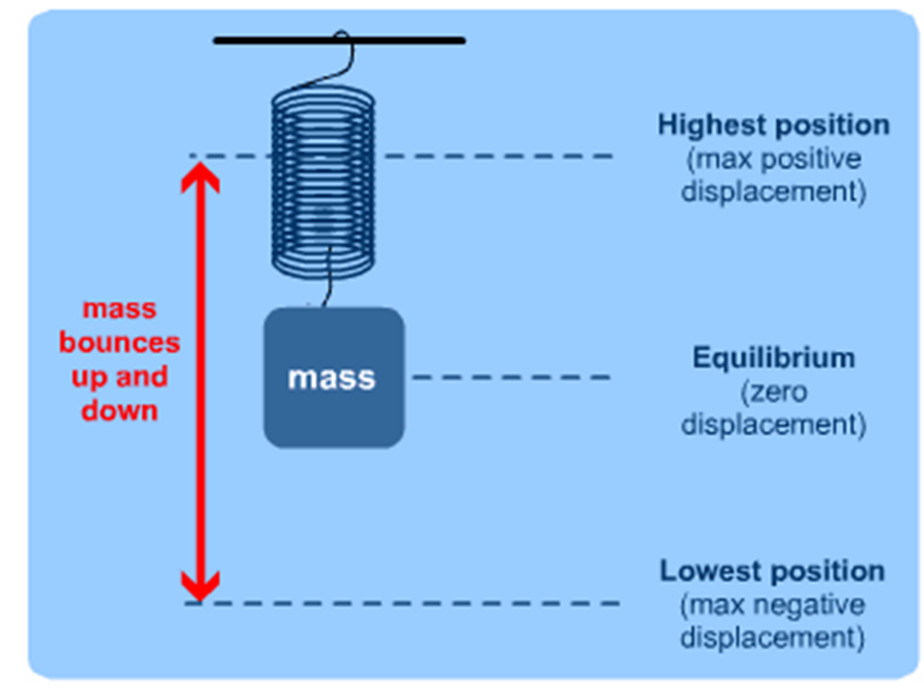
The displacement of an oscillating particle is the distance the particle has been moved from its equilibrium position.
一个振动质点的位移就是距离其平衡位置的距离。
The amplitude of an oscillation is the maximum displacement of the vibrating object from the equilibrium position (its usual position).
振幅就是指点质点距离其平衡位置的最大距离。
Note: Always check the x-axis on the graph, as it is easy to confuse wavelength and time period on diagrams!
l Simple Harmonic Motion 简谐运动
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) is a particular type of oscillation. It is useful because its time period stays the same even when its amplitude changes.
是最基本也是最简单的一种机械振动。当某物体进行简谐运动时,物体所受的力跟位移成正比,并且力总是指向平衡位置。
Lets think about a simple example of SHM to work out the relationship between displacement, velocity and acceleration:
思考下面这个简单的简谐运动模型的例子,这将有助于我们进一步理解SHM
Now remember that displacement, velocity and acceleration are all vectors, and as a result, direction is important. Let's choose anything in the up-wards direction to be positive, anything downwards to be negative. (If you decide to do the opposite, it doesn't matter - just stick to your choice.)
记住,简谐运动中,位移,速度,和加速度都是向量,方向的选择也是尤为重要的。让我们选向上为正方向,向下为相反方向
If we set this system oscillating by lifting the mass and letting it go, then the system starts with: Maximum positive displacement (because it's above the middle).
如果我们事先已经把弹簧下面的物块拉离平衡位置,那么整个物理系统此时处于的位置就是最大位移
Zero velocity (it's not moving at the first instant).
此时,速度为零
Maximum negative acceleration (because it is about to start moving down).
但是拥有最大的加速度,指向为负方向
The interaction below shows how velocity and acceleration change in simple harmonic motion. It shows the relationship between velocity and acceleration.
The displacement, velocity and acceleration of the mass are related as shown above. To draw these, think about what the object is doing at each point as it oscillates from the start position described above.
下面的相互作用力示意图展示了速度与加速度在简谐运动中如何变化,也就是速度与加速度,位移与速度和加速度与质量之间的关系,为了准确理解,我们就需要知道这个质点在每一点的运动规律与离开开始位置的距离。
As it passes through the equilibrium position on the way down it's at maximum speed down (negative), its displacement is zero and because the spring is at its equilibrium position, there is no resultant force on the mass so it is not accelerating.
质点移动到平衡点位置时,位移为零,速度达到最大,不受力。
At the bottom, the mass stops momentarily as it changes direction, so velocity is zero. The displacement is a maximum in the negative direction, so the acceleration is a maximum in a positive direction as the spring tries to shorten again.
质点移动到最低点时,质点速度为零,位移为负,加速度达到最大。
1. The velocity, v, is zero where there are stationary points at the peaks and troughs of the displacement graph and the velocity is a maximum when the displacement is zero. (Don't forget the gradient of the displacement graph will equal velocity.)
速度为零的时候,是简谐运动停止的时候,位于波谷与波峰反映在位移与速度的图像上,换句话说就是速度等于零的时候位移达到最大。
2. The displacement and acceleration graphs are 180 degrees out of phase and therefore look like a mirror image of each other in the time axis. (Don't forget the gradient of the velocity graph will equal acceleration.)
位移与加速度的相位相差180度,就像镜面对称一样。
Definition of Simple Harmonic Motion: 简谐运动正式定义
A body is undergoing SHM when the acceleration on the body is proportional to its displacement, but acts in the opposite direction.
如果一个物体在外力作用下,其加速度与它的位移成正比例关系,并且其所受力的方向与位移的方向相反,那么它的运动规律就是简谐运动。
Acceleration is proportional to displacement
加速度与位移成正比例关系
a α - s
It's also important to note that for SHM, the time period of the oscillations is constant and doesn't change even if the amplitude is changing.
特别需要注意的是,简谐振动的周期是一个与其振幅无关的物理量,它不随振幅的变化而变化。
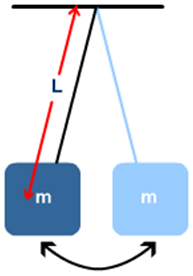
There are two common examples of simple harmonic motion:
有两种典型的做简谐运动的例子
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Where m = mass (kg) and k = spring constant (Nm-1) |
Where L = length of pendulum (m) g = acceleration due to gravity (ms-2) |
SHM is used to explain the behaviour of atoms in a lattice, which oscillate like masses on springs.
简谐运动也被用来解释晶体内的原子振动规律,与弹簧振子的规律是一样的。
其实生活中还有很多的运动的规律都可以归咎为简谐运动,所以说我们对于物理的理解可不要仅仅停留在卷面上啊。
最后祝大家在A Level考试中都能拿到A*!!!
上述就是今天介绍的主要内容,如果对此内容有疑问,欢迎在线咨询我们的课程顾问老师,A+国际教育中心是国内领先的国际课程辅导机构,专注于为中小龄学员提供国际课程辅导,包括ks1-ks3、GCSE、IGCSE/Pre-A、A-Level、AP、IB等课程学科辅导,同时为申请英美澳加等国家私立初高中的学生提供入学考试辅导,帮助学生顺利入读国外优秀私立学校。目前在北京、英国、美国分别设有授课中心。
 喜欢 [0]
喜欢 [0] 相关推荐

- GCSE心理考试这么写
知识点 2021-02-18

- GCSE英语考试考不好?
知识点 2021-02-18

- GCSE成绩不满意可以重审吗?一定要重考吗?
知识点 2021-02-18

- 申请英国大学必须要用gcse吗
知识点 2021-12-16